Table of Contents [expand]
- Popular use cases
- Provisioning the add-on
- Free Trial
- Dashboard
- Importing jobs
- Defining Jobs
- Cron expression examples
- Rate expression examples
- Monitoring and logging
- Killing jobs
- Notifications
- Webhooks
- Long running jobs
- API Access
- Heroku CLI Plugin
- Using Cron To Go with Rails
- Using Cron To Go with Node.js
- Migrating between plans
- Removing the add-on
- Debugging failed jobs
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Known issues
- Support
Last updated March 13, 2025
Cron To Go is an add-on created for Heroku users to run scheduled jobs based on one-off dynos using cron expressions or time intervals, up to once per minute.
Cron To Go combines the simplicity of using cron to schedule jobs with the scale and elasticity of the cloud. Instead of running always-on processes, Cron To Go provides the option to start one-off dynos only when you need them. Another benefit of using Cron To Go over code-based schedulers is that you don’t need to deploy new code when you have to make changes or additions to your scheduled jobs - simply add, edit or delete a job from the Cron To Go dashboard.
In addition to your Cron To Go plan’s price, you will be billed for the amount of one-off dynos executed by the scheduler.
Cron To Go relies on Heroku APIs for job execution. If the APIs are unavailable, scheduled job execution might be skipped. If scheduled jobs are critical to your application, it is recommended to run a custom clock process instead.
Popular use cases
Using feedback and data collected over time, we have highlighted the top use cases of our clients up to date: or Examples of use cases that Cron To Go is most commonly used for include:
- Running periodic SQL statements on Heroku Postgres. You can refresh materialized views, run cleanup statements to get rid of unwanted data, or perform BI processes such as in-database transformations. The following example makes use of psql command line with the DATABASE_URL environment variable to refresh a materialized view:
psql $DATABASE_URL -c "REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW vw_account_counters" - Hitting HTTP endpoints. You can easily make HTTP(S) requests to your web API or 3rd party API endpoints using Curl to start application processes. The following example uses curl to reach a 3rd party endpoint:
curl http://itsthisforthat.com/api.php?json - Scheduling periodical batch jobs. Jobs such as grabbing orders from Shopify, generating weekly reports, or sending email notifications to application users by running your own code are made possible. The examples below show how to run Rails and Node apps using Cron To Go.
Provisioning the add-on
Quick and easy set up begins by attaching Cron To Go to a Heroku application via the following CLI:
A list of all plans available can be found here.
$ heroku addons:create crontogo
-----> Adding crontogo to sharp-mountain-4005... done, v18 (free)
After you have provisioned Cron To Go, the dashboard is accessible for your use. You can now get started on defining and scheduling jobs.
Free Trial
Before deciding on a plan that best suits you, we offer a free trial that allows you to explore all of the features included in the Gold plan for 7 days. This includes up to 50 jobs, unlimited number of executions, email notifications, webhooks and more. After the 7 day-trial is up, the jobs are automatically disabled and you will only be able to run ad-hoc jobs, unless you have enabled the jobs through an upgrade to a paid plan of your choice.
A list of all available plans and information can be found here. Our plans range, consisting of a variety of features and purposes. Further support from our customer service team is available to help you find the most suitable plan according to your needs.
Dashboard
The Cron To Go dashboard allows you to:
- Create jobs
- Import jobs from other scheduling systems
- Edit job definitions
- Delete jobs
- Duplicate a job to create a new job based on an existing job
- Pause an active job
- Resume an inactive job
- View job logs
- View job history - see previous job executions, status and duration
- Change notification settings
You can access the dashboard via the CLI:
$ heroku addons:open crontogo
Opening crontogo for sharp-mountain-4005
or by visiting the Heroku Dashboard and selecting the application in question and then clicking Cron To Go in the Add-ons menu.
Importing jobs
Click the import button for a smooth migration of jobs from other scheduling systems:
- Heroku Scheduler
- Temporize
- Advanced Scheduler
- Cron To Go (import jobs from your other Cron To Go instances)
With a single click, you can import all defined jobs within your app’s Heroku Scheduler in order to monitor and manage all your jobs in a single place. Additionally, you can define your job schedules using cron expressions or rate expressions, and with the maximum precision of 1 minute.
Defining Jobs
Cron To Go Jobs consist of the following:
- Optional nickname (for example,
Daily ETL). - Job schedule (in cron expression format or rate expression format). The smallest run time interval available is one minute.
- Timezone. UTC is the default timezone.
- Jitter - The amount of jitter to add to the schedule. This is useful in cases that requires dispersing job invocations. For example, if you configure a 15 minute jitter for a schedule that runs every hour, it invokes the job within 15 minutes after the next run.
- Command to execute.
- Process type - For container based apps only, you can specify the process type to use for the one-off dyno. For example,
web,worker,release, etc. Read more about Container based apps here. - Size of one-off dyno to execute the command in. Read more about available one-off dyno sizes here.
Only customers with an established payment history with Heroku (paying for hobby, 1X/2X dynos, Heroku Data and other add-ons) can use performance-tier dynos. Read more here.
- One-off dyno timeout in seconds. Sets the time for the one-off dyno to expire, after which it will be killed. You can read more about it here.
When triggered, these jobs run in one-off dynos and show up in your logs as a dyno named crontogo_[job_id].
Cron expression examples
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
*/5 * * * * |
every 5 minutes |
*/5 * * * 1-5 |
every 5 minutes on weekdays (Monday-Friday) |
0 1 * * 5 |
every Friday at 1am |
10 */1 * * * |
once an hour, at xx:10 |
You can use Cron Expression To Go to generate other cron expressions.
Rate expression examples
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
Every 7 minutes |
every 7 minutes |
Every 5 hours |
every 5 hours |
Every 3 days |
every 3 days |
The examples above are hard to accomplish with cron expressions. See here for more information.
Monitoring and logging
One-off dynos that execute as part of Cron To Go output their logs with the process: crontogo_[job_id].
To retrieve the logs for the dynos started by Cron To Go, run the following command line:
$ heroku logs -t -a <app-name> -d crontogo
Use the Cron To Go dashboard to view the streamed dyno log from Heroku by clicking the ... button and select View job logs or View job history.
Job logs are pulled directly from your app logs and are not stored by Cron To Go. Due to Heroku’s log history limits, logs may not be available. For more production-ready persistence of logs, we recommend to use one of the Heroku platform’s available logging add-ons to your app.
Killing jobs
To stop a job that is currently running:
- Click the job’s
actionsmenu and thenView job history. - The dialog that opens shows a list of the recent executions of the job. Look for the running job execution that you would like to stop.
- Click the
...menu button and thenStop. - Confirm to proceed with stopping the execution.
- The job status will change from
runningtostopping. - When the job is stopped, the job status will change to
failed(with process status 143 - SIGTERM) and theStop requestfield will indicate when Cron To Go has requested to stop the job execution.
Notifications
Cron To Go monitors your job executions and determines execution status using Heroku’s API response status code and the process exit code. When a process exits with code 0 (zero), execution is successful. Otherwise, if the API response status code is not 2xx or the process exit code is greater than 0, the job is marked as failed.
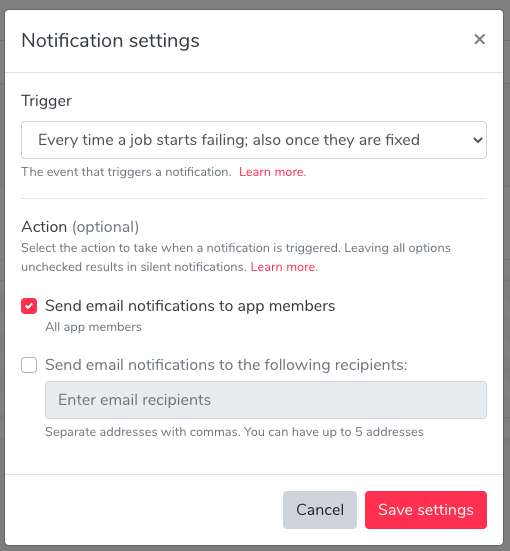
By default, app members of plans that support notifications will receive email notifications every time a job starts to fail and additionally when the job completes successfully after one or more consecutive failures.
You can change these settings by clicking Settings in dashboard top menu:
- Change the notification trigger, to permit email notifications only when jobs start to fail.
- Set recipient emails manually (the preferred approach is to use your email platform to create an alias and manage group membership instead of managing email lists in Cron To Go).
- Silence notifications by deselecting both app members and email recipients.
Webhooks
Webhooks enable you to receive notifications whenever particular events occur with your jobs. You can subscribe to notifications regarding the following events:
- Job execution failed - occurs whenever a job execution fails to complete.
- Job execution started - occurs whenever a job execution is started.
- Job execution succeeded - occurs whenever a job execution completes successfully.
Webhook notifications are sent as HTTP POST requests to a URL of your choosing. To integrate with webhooks, you need to implement a server endpoint that receives and handles these types of requests.
Please note that our webhooks don’t work with self-signed certs. If a webhook detects a self-signed cert, it will result in an error and no request will be sent.
To subscribe to webhooks, go to the webhooks interface in the dashboard by clicking Webhooks. Then, click the Add webhook button.
Once the dialog opens, fill out the following:
Nickname(optional) - a descriptive name for your webhook.EndpointType- select one of the supported endpoint types:Webhook- send a HTTP POST requests to the endpoint URL.Slack- send a Slack message to the endpoint URL which should be a valid Slack incoming webhook URL.Teams- send a Microsoft Teams message to a Teams incoming webhook URL.Email- send a notification to an email recipient.
URL- For Webhook, this should be a valid HTTPS URL that will receive webhook notifications. For Slack and Teams, this should be a valid incoming webhook URL.Email- An email address of a recipient that will receive all webhook notifications for Email types. An address with display name is also supported (e.g.Display Name <email-address>).
Authorization Header(optional) - a customAuthorizationheader that will be included with all webhook notifications.Topics- select the types of notifications you want to be informed about. You must include at least one topic.Filter- apply filtering rules to trigger notifications that meet the specified criteria, i.e. have (or don’t have) certain properties.
Finish by clicking Add webhook.
Securing Webhooks
When a webhook is created, a signing secret is generated and displayed once.
Each request is signed by Cron To Go in the X-Hub-Signature header. If you wish to verify the authenticity of our request, copy the signing secret provided and use it to verify the webhook signature. You can rotate the signing secret at any time to obtain a new one.
You may also use an authorization header to verify that the request came from Cron To Go. If properly set, the authorization header is passed through the Authorization header found in the request. It should be validated using the authorization mechanism of your choice on your server.
Managing Webhooks
After successfully creating a webhook, you may initiate the following:
- Pause/Resume - temporarily pause webhook notifications or resume them.
- Rotate secret - see Securing Webhooks
- Test webhook - manually send a test event to your endpoint
- View deliveries - View a log of the notifications that Cron To Go has enqueued to be sent. Each notification has a
status(consisting ofSucceeded,Failed, and ‘Pending’ categories),Createdtimestamp,ID,Topic(one ofjob.execution.failed,job.execution.started,job.execution.succeeded,webhook.ping) andDuration. You may also view theRequest payload,Response codeandResponse body, or manually send a webhook payload from within the webhook delivery dialog.
Receiving Webhooks
When a webhook event that you’ve subscribed to occurs, Cron To Go sends a POST request to your server endpoint with the details of the event.
You can verify the authenticity of these requests in any of the following ways:
- The request’s Authorization header matches the value you provided when subscribing to notifications.
- The request’s X-Hub-Signature header contains the HMAC SHA256 signature of the request body (signed with the secret value provided when subscribing).
A resulting webhook notification request resembles the following:
POST https://webhook.site/394f2074-e56f-4110-7bf7-ca14a1f48b7c
Authorization: Bearer 01234567-89ab-cdef-0123-456789abcdef
X-Hub-Signature: cLcN5U5x+jHEkANnVaaRwBw7yE4uv4pXdjcY9Cajc7M=
{
"Metadata": {
"Webhook": {
"Id": "6b1c6f0c-52c1-47a6-9344-57a4579ced68"
},
"Delivery": {
"Id": "c7ce90e6-5708-43b1-a052-13991f45c771"
},
"Attempt": {
"Id": "2e241efe-d22f-4fe7-aab9-adcde63fca6d"
},
"Event": {
"Id": "2e579289-4c4a-4085-9b43-74020865cdda",
"Topic": "webhook.ping"
}
},
"CreatedAt": 1590911947688,
"Resource": "webhook",
"PreviousData": null,
"Data": {
"Topics": [
"job.execution.succeeded",
"job.execution.failed",
"job.execution.started"
],
"State": "paused",
"Alias": "Test Webhook",
"CreatedAt": 1590501031122,
"Id": "6b1c6f0c-52c1-47a6-9344-57a4579ced68",
"OrganizationId": "d57060b1-23fe-2d59-afd0-7f56d9e1fc55",
"UpdatedAt": 1590911941179,
"Url": "https://webhook.site/394f2074-e56f-4110-7bf7-ca14a1f48b7c"
},
"Id": "2e579289-4c4a-4085-9b43-74020865cdda",
"Topic": "webhook.ping",
"UpdatedAt": 1590911947688
}
You should always respond with a 200-level status code to indicate that you had received the notification. Cron To Go ignores the body of your response by default, so a 204 status with an empty body is ideal:
204 No Content
If you do not return a 200-level status code, Cron To Go records the failure. The failure status can be viewed in the deliveries log.
job.execution.started Event Format
{
"Id": "22e45a18-0a91-470d-b0d4-846b2fa832cb",
"Topic": "job.execution.started",
"CreatedAt": 1590591047428,
"UpdatedAt": 1590591047428,
"Resource": "JobExecution",
"PreviousData": null,
"Data": {
"AttemptsCount": 1,
"TriggerType": "manual",
"Target": {
"Type": "dyno",
"TimeToLive": 1800,
"AppId": "22e1e196-fbc6-4091-af57-8d7ad63aa7d3",
"Command": "python run_etl.py",
"Size": "Hobby"
},
}
"State": "running",
"CreatedAt": 1590591046983,
"Id": "43668791-ce11-4994-9e91-fc8fda310614",
"OrganizationId": "d57060b1-23fe-2d59-afd0-7f56d9e1fc55",
"NextAttemptAt": null,
"UpdatedAt": 1590591046983,
"JobId": "6069e1c0-280d-22a3-93ce-159d9a60924d",
"LastAttempt": {
"State": "running",
"CreatedAt": 1590591046512,
"Id": "a28c2010-549c-4253-a869-42b748998477",
"StatusCode": 201
},
"Metadata": {
"Webhook": {
"Id": "6b1c6f0c-52c1-47a6-9344-57a4579ced68"
},
"Delivery": {
"Id": "e69d0b8a-447d-4ddc-a21a-704630272353"
},
"Attempt": {
"Id": "7ecb9953-dd36-4309-8db6-0043f989b7aa"
},
"Event": {
"Id": "22e45a18-0a91-470d-b0d4-846b2fa832cb",
"Topic": "job.execution.started"
}
},
}
job.execution.succeeded Event Format
{
"Id": "5b8f2e1c-4a53-4db6-b6ae-a88786f77459",
"Topic": "job.execution.succeeded",
"CreatedAt": 1590591016589,
"UpdatedAt": 1590591016589,
"Resource": "JobExecution",
"PreviousData": null,
"Data": {
"AttemptsCount": 1,
"TriggerType": "schedule",
"Target": {
"Type": "dyno",
"TimeToLive": 1800,
"AppId": "22e1e196-fbc6-4091-af57-8d7ad63aa7d3",
"Command": "python run_etl.py",
"Size": "Hobby"
},
"State": "succeeded",
"CreatedAt": 1590591011407,
"Id": "acc83806-505c-46a1-b9a9-04025f7d66fe",
"OrganizationId": "d57060b1-23fe-2d59-afd0-7f56d9e1fc55",
"NextAttemptAt": null,
"UpdatedAt": 1590591016222,
"JobId": "6069e1c0-280d-22a3-93ce-159d9a60924d",
"LastAttempt": {
"ExitStatus": 0,
"State": "succeeded",
"CreatedAt": 1590591011017,
"Id": "2f858f6e-1adb-46ac-945f-b86230ec2076",
"StatusCode": 201
}
},
"Metadata": {
"Webhook": {
"Id": "6b1c6f0c-52c1-47a6-9344-57a4579ced68"
},
"Delivery": {
"Id": "277d0c61-1eff-46f2-8e8a-22d9c144d11c"
},
"Attempt": {
"Id": "6c6128fd-ca7f-4828-997f-0084cc15d4b1"
},
"Event": {
"Id": "5b8f2e1c-4a53-4db6-b6ae-a88786f77459",
"Topic": "job.execution.succeeded"
}
}
}
job.execution.failed Event Format
{
"Id": "265a4af1-7db2-41ad-a3d1-79f7ef2b20ac",
"Topic": "job.execution.failed",
"CreatedAt": 1590591051225,
"UpdatedAt": 1590591051225,
"Resource": "JobExecution",
"PreviousData": null,
"Data": {
"AttemptsCount": 1,
"TriggerType": "manual",
"Target": {
"Type": "dyno",
"TimeToLive": 1800,
"AppId": "22e1e196-fbc6-4091-af57-8d7ad63aa7d3",
"Command": "python run_etl.py",
"Size": "Hobby"
},
"State": "failed",
"CreatedAt": 1590591046983,
"Id": "43668791-ce11-4994-9e91-fc8fda310614",
"OrganizationId": "d57060b1-23fe-2d59-afd0-7f56d9e1fc55",
"NextAttemptAt": null,
"UpdatedAt": 1590591051024,
"JobId": "6069e1c0-280d-22a3-93ce-159d9a60924d",
"LastAttempt": {
"ExitStatus": 7,
"Message": "Process exited with status 7",
"State": "failed",
"CreatedAt": 1590591046512,
"Id": "a28c2010-549c-4253-a869-42b748998477",
"StatusCode": 201
}
},
"Metadata": {
"Webhook": {
"Id": "6b1c6f0c-52c1-47a6-9344-57a4579ced68"
},
"Delivery": {
"Id": "a03167ee-e26c-47dc-a798-f3fa4eb2a41d"
},
"Attempt": {
"Id": "c56f1bbf-b154-4f0b-96dd-d500946cbd55"
},
"Event": {
"Id": "265a4af1-7db2-41ad-a3d1-79f7ef2b20ac",
"Topic": "job.execution.failed"
}
}
}
webhook.ping Event Format
{
"Id": "2e579289-4c4a-4085-9b43-74020865cdda",
"Topic": "webhook.ping",
"CreatedAt": 1590911947688,
"UpdatedAt": 1590911947688,
"Resource": "webhook",
"PreviousData": null,
"Data": {
"Topics": [
"job.execution.succeeded",
"job.execution.failed",
"job.execution.started"
],
"State": "paused",
"Alias": "Test Webhook",
"CreatedAt": 1590501031122,
"Id": "6b1c6f0c-52c1-47a6-9344-57a4579ced68",
"OrganizationId": "d57060b1-23fe-2d59-afd0-7f56d9e1fc55",
"UpdatedAt": 1590911941179,
"Url": "https://webhook.site/394f2074-e56f-4110-7bf7-ca14a1f48b7c"
},
"Metadata": {
"Webhook": {
"Id": "6b1c6f0c-52c1-47a6-9344-57a4579ced68"
},
"Delivery": {
"Id": "c7ce90e6-5708-43b1-a052-13991f45c771"
},
"Attempt": {
"Id": "2e241efe-d22f-4fe7-aab9-adcde63fca6d"
},
"Event": {
"Id": "2e579289-4c4a-4085-9b43-74020865cdda",
"Topic": "webhook.ping"
}
}
}
Long running jobs
You can control the maximum execution time for a job using the timeout setting for each job. To ensure that only one instance of a job executes, set the timeout to a value lower than the frequency in which the job executes, as set by the cron expression.
Dynos in private spaces take a few minutes before they start running. If you set the timeout to a low value (i.e. less than 4 minutes), the TTL set for the one-off dyno may leave the dyno in an inconsistent state. This may result in the inability of the dyno to terminate and the accumulation of one-off dynos, which may then further result in an error (Cannot run more than X <type> size dynos) affecting future job executions.
API Access
The environment variables CRONTOGO_API_KEY and CRONTOGO_ORGANIZATION_ID are added to the app when Cron To Go add-on is provisioned and are used for API access. Read more about Cron To Go API here.
Heroku CLI Plugin
Cron To Go can also be managed using an Heroku CLI plugin. The Heroku CLI plugin can be used to create, manage, run and monitor jobs, or import jobs into Cron To Go using a manifest file as part of a post deploy script. For more details see Cron To Go CLI Reference.
To install the plugin:
$ heroku plugins:install heroku-cron
To get the plugin documentation run:
$ heroku cron:jobs --help
list jobs on Cron To Go
USAGE
$ heroku cron:jobs
OPTIONS
-a, --app=app (required) app to run command against
-r, --remote=remote git remote of app to use
-x, --extended show extra columns
--columns=columns only show provided columns (comma-seperated)
--csv output is csv format
--json return the results as JSON
--no-header hide table header from output
--no-truncate do not truncate output to fit screen
DESCRIPTION
Read more about this feature at https://devcenter.heroku.com/articles/crontogo
EXAMPLES
$ heroku cron:jobs -a your-app
$ heroku cron:jobs --app your-app --json
$ heroku cron:jobs --app=your-app --csv
COMMANDS
cron:jobs:clear delete all jobs on Cron To Go
cron:jobs:create create a job on Cron To Go
cron:jobs:delete delete job on Cron To Go
cron:jobs:import import jobs into Cron To Go using a [manifest file](https://github.com/crazyantlabs/heroku-cli-plugin-cron/blob/main/examples/manifest.yml)
cron:jobs:info get information about a job on Cron To Go
cron:jobs:logs display job recent log output on Cron To Go
cron:jobs:pause pause job on Cron To Go
cron:jobs:resume resume job on Cron To Go
cron:jobs:run trigger job execution on Cron To Go
cron:jobs:update update a job on Cron To Go
Using Cron To Go with Rails
Cron To Go can run any command that may be run in your application. In Rails, the convention is to set up rake tasks. To create tasks in Rails, copy the code below to lib/tasks/scheduler.rake and customize it to fit your needs:
desc "This task is called by the Cron To Go"
task :eat_breakfast => :environment do
puts "Eating breakfast..."
Kitchen.eat
puts "done."
end
task :exercise => :environment do
puts "Starting workout..."
Gym.workout
puts "done."
end
After writing a task and deploying it to Heroku, you can test it using heroku run:
$ heroku run rake eat_breakfast
After testing on Heroku, you can add a job to Cron To Go that specifies
rake eat_breakfast as the command to run.
Using Cron To Go with Node.js
Cron To Go can run any command that can be run in your application. For Node.js, you can simply add a file to your app called schedules.js and execute it:
module.exports.eat_breakfast = function()
{
console.log('Eating breakfast...');
Kitchen.eat();
console.log('done.');
}
require('make-runnable');
After writing your task and deploying it to Heroku, test it using heroku run:
$ heroku run node schedules.js eat_breakfast
After testing on Heroku, you can add a job to Cron To Go that specifies
node schedules.js eat_breakfast as the command to run.
Migrating between plans
You can either use the UI to upgrade or downgrade current Cron To Go plan, or use the heroku addons:upgrade command to migrate to a new plan.
$ heroku addons:upgrade crontogo:gold
-----> Upgrading crontogo:newplan to sharp-mountain-4005... done, v18 ($49/mo)
Your plan has been updated to: crontogo:gold
Removing the add-on
You can remove Cron To Go via the CLI:
This will destroy all associated data and cannot be undone!
$ heroku addons:destroy crontogo
-----> Removing crontogo from sharp-mountain-4005... done, v20 (free)
Debugging failed jobs
Jobs may fail due to Heroku errors or application errors.
Heroku errors may indicate a service-wide error (e.g. "Service temporarily unavailable. Please try again later") or errors that have to do with the dyno type you chose ("Requested type Standard-1X is not available. Please use Hobby" or "Cannot run more than 1 Free size dynos."). In such cases, make sure to select a dyno type that conforms with your app and that you adhere to the limit on concurrent dynos of the selected type. You can do this by either changing your job schedules to make sure there are less concurrent jobs using this dyno type, or you may ask Heroku to increase your limit. Click here for more information on how to get this done.
In the instance your job fails due to application errors, you can check your application logs in Cron To Go by clicking View Job Logs in the job’s Actions menu or by searching for the job id in your logging add-on.
You may also want to reproduce the error by running the job command using heroku run - simply copy the command and run it in your terminal to find the culprit. For example:
$ heroku run python db-cleanup.py --size Hobby --timeout 1800 --app cyberdyne-backoffice
Running python db-cleanup.py --timeout 1800 on ⬢ cyberdyne-backoffice... up, run.9986 (Hobby)
python: can't open file 'db-cleanup.py': [Errno 2] No such file or directory
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: In Cron To Go, I can only select Hobby/Free dynos, but when trying to run the job I get the following error: Requested type Hobby is not available. Please use Standard-1X, etc.
A: Cron To Go shows the dyno types available for your app. This message most likely indicates that you should add a procfile to your app. After adding it, you will have access to select the appropriate dyno type.
Q: I get the error Cannot run more than X <type> size dynos. What can I do?
A: There are limits imposed by Heroku on the concurrent number of one-off dynos you are permitted to use. To remedy this issue, either change the dyno type or the frequency of your jobs, or request Heroku to increase your limits. In addition, if you use private space dyno types with low timeout values, this may also be a possible cause (See Long Running Jobs).
Q: My job fails with the message process exited with status 143. What can I do?
A: When a dyno in Heroku receives a SIGTERM signal, which is a signal to terminate, it will stop the process and exit with exit code 143. A dyno in Heroku can receive a SIGTERM signal for various reasons - manual termination (stopping the job from Cron To Go, or using heroku ps CLI), Heroku maintenance, memory or CPU quota exceeded, environment changes or application updates. In addition, when a job reaches its timeout, it also receives a SIGTERM. Check if increasing the timeout is required, or if your job needs more resources.
Q: I’m using Cron To Go with PHP and I don’t see anything in my job logs. What’s wrong?
A: Artisan seems to append > '/dev/null' 2>&1 to the command you run. A possible solution is outlined here.
Q: How do I change my email notification settings?
A:
First, go to your Heroku app dashboard (the app where Cron To Go is installed), find Cron To Go under Installed add-ons and click it to open Cron To Go dashboard.
Click the Settings menu item:
Scroll to the notifications section to change the notification recipients and click save:
Q: How do I disable Datadog’s agent on my Cron To Go job dynos?
A: If you want to avoid being charged for Datadog’s agent running on your Cron To Go job dynos, add the following lines to your pre-run script:
# Disable the Datadog Agent based on dyno type
if [[ "$DYNOTYPE" == "crontogo"* ]]; then
DISABLE_DATADOG_AGENT="true"
fi
Known issues
Cron To Go and Container Registry
If you are using Cron To Go and Container Registry as your deployment method, your process must be accessible from the web image. If your job requires a custom process type, use the Process type field of the job to specify the process type other than web.
Support
All Cron To Go support and runtime issues should be submitted via one of the Heroku Support channels. Any non-support related issues or product feedback is welcome at support@crontogo.com.