Last updated February 13, 2026
This integration is only available for Heroku Enterprise customers.
The Heroku GitHub Enterprise Server Integration is the recommended way to integrate with GitHub. It uses GitHub Apps, which are more secure compared to personal OAuth tokens and offer more granular permissions. Using the integration, you don’t need to maintain a service account as a separate user as the GitHub app acts on its own behalf, taking actions via the API directly using its own identity.
This integration provides the following advantages over Heroku GitHub Deploys:
- If the user who set up the integration leaves the GitHub org, deploys still work
- Allow for more permissions and control for repos
After installing the integration on an Enterprise account, all Enterprise teams under that account must use this GitHub Enterprise Server integration for any new apps or pipelines.
Prerequisites
To set up the integration, you must have:
- the
managepermission for an active Heroku Enterprise account - full access to the GitHub Enterprise Server org that contains all the repos you want to use with this integration
- no unowned pipelines
- have the expiring user access tokens feature disabled in GitHub
If you have just closed your contract or are currently transitioning to Enterprise, wait for your Enterprise account to be created.
Enable the Integration
Apps under a specific team can only use GitHub Enterprise or GitHub.com. We implemented a safety process that requires customers to reach out to Heroku Support with the name or ID of your Enterprise account to enable the integration. After installing on an Enterprise account, all teams under that account must use the GitHub Enterprise Server integration for new apps or pipelines, unless you ask Heroku to enable the integration for specific teams only.
Testing with Only Specific Teams
It’s not easy to switch back to using personal OAuth tokens for GitHub. We highly recommend testing, especially if you have more than 20 pipelines. You can create a new Enterprise team for testing, or use an existing one with non-critical apps and pipelines. Contact Heroku with the name of the team you want to test so that we only enable the integration for that team in your account. Only users in the test Enterprise team can see the new integration and use it for new pipelines. They can also update existing pipelines from legacy OAuth connections to the new integration.
If the integration works as expected after completing testing, contact Heroku again to enable the feature for all teams in your account.
Set Up the Integration
After configuring this integration, there’s no easy way to switch back to your old configuration. Uninstalling the integration means disconnecting all your apps and pipelines and manually reconnecting to use personal OAuth tokens with Heroku GitHub Deploys.
Installing the integration doesn’t disconnect any existing connections with GitHub, but you must reconfigure any apps and pipelines you want to use this GitHub Enterprise Server integration.
You can install the integration from the Enterprise account’s Settings tab. All users with manage permission at the Enterprise account level can see the installation option.
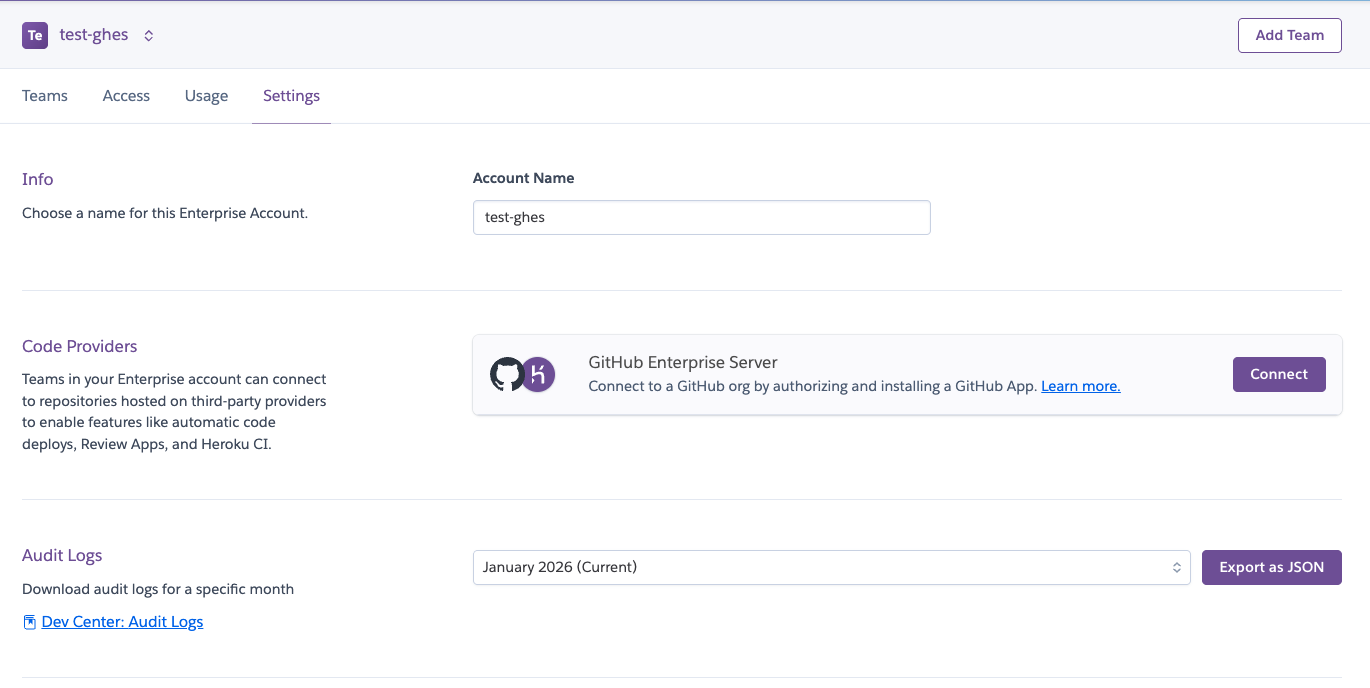
Select Connect to get promoted for the url for the GitHub Enterprise Server and the name of the organization (within the GitHub Enterprise Server) that you want to install the GitHub App on, in order to start the app installation process.
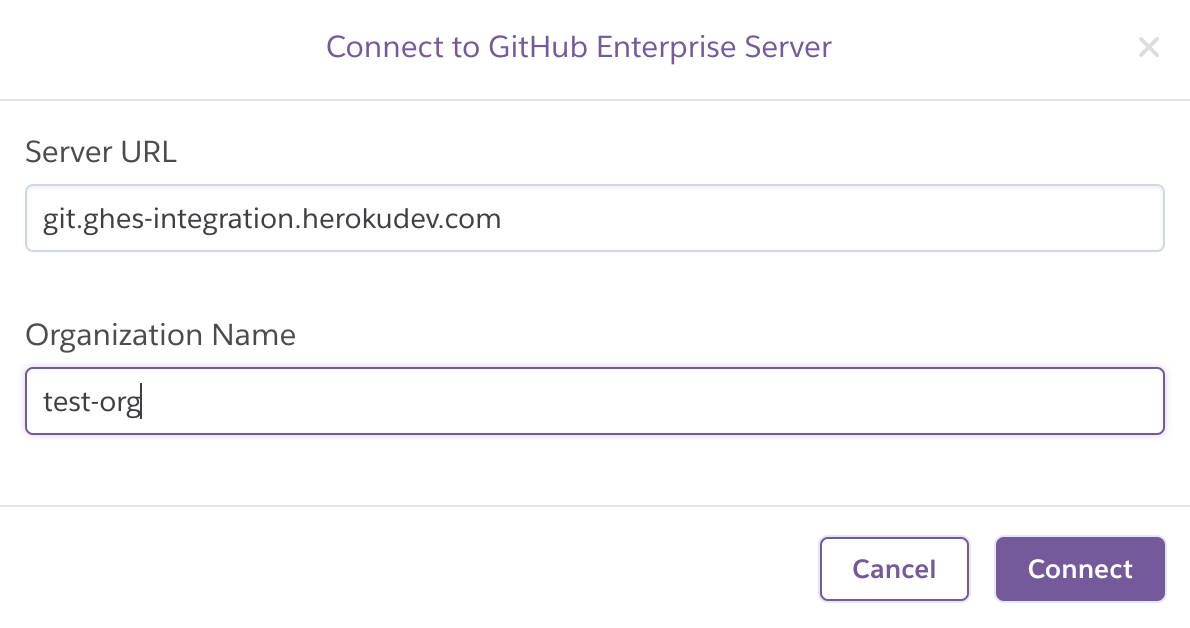
After filling out the modal and selecting Connect, you get redirected to the GitHub Enterprise Server to complete the GitHub App installation process.
Provide a name for this app and select Create GitHub App.
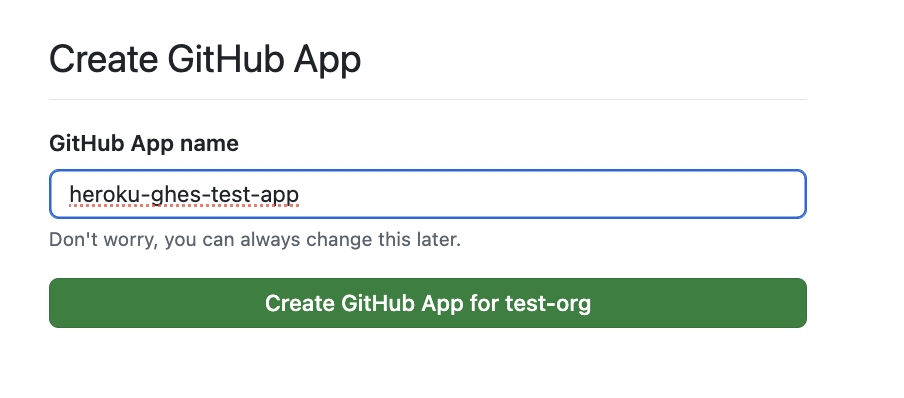
All the repositories used across the entire Enterprise Account must be under the same GitHub org for this installation to work correctly.
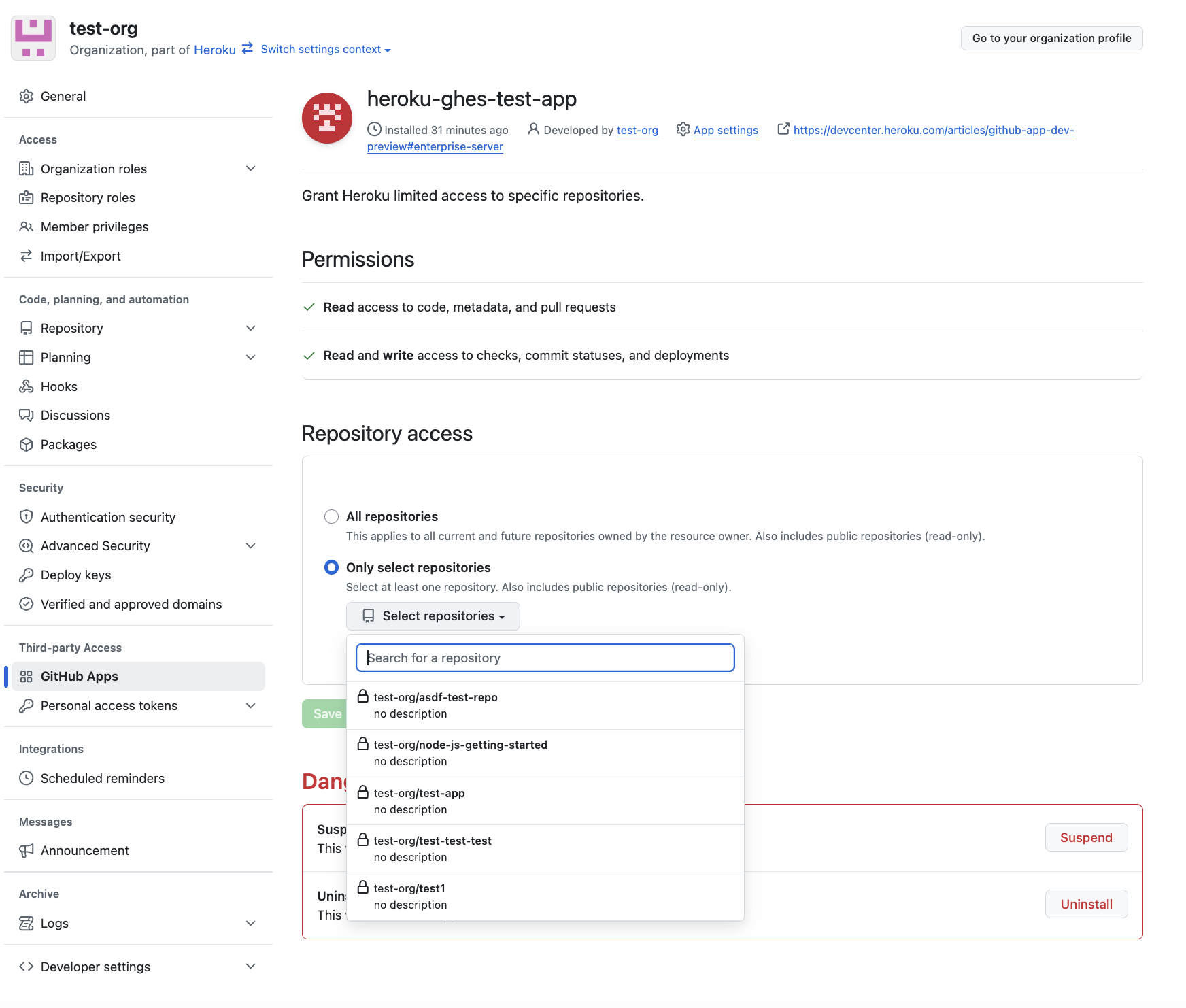
Next, select all or a specific set of repositories to allowlist: 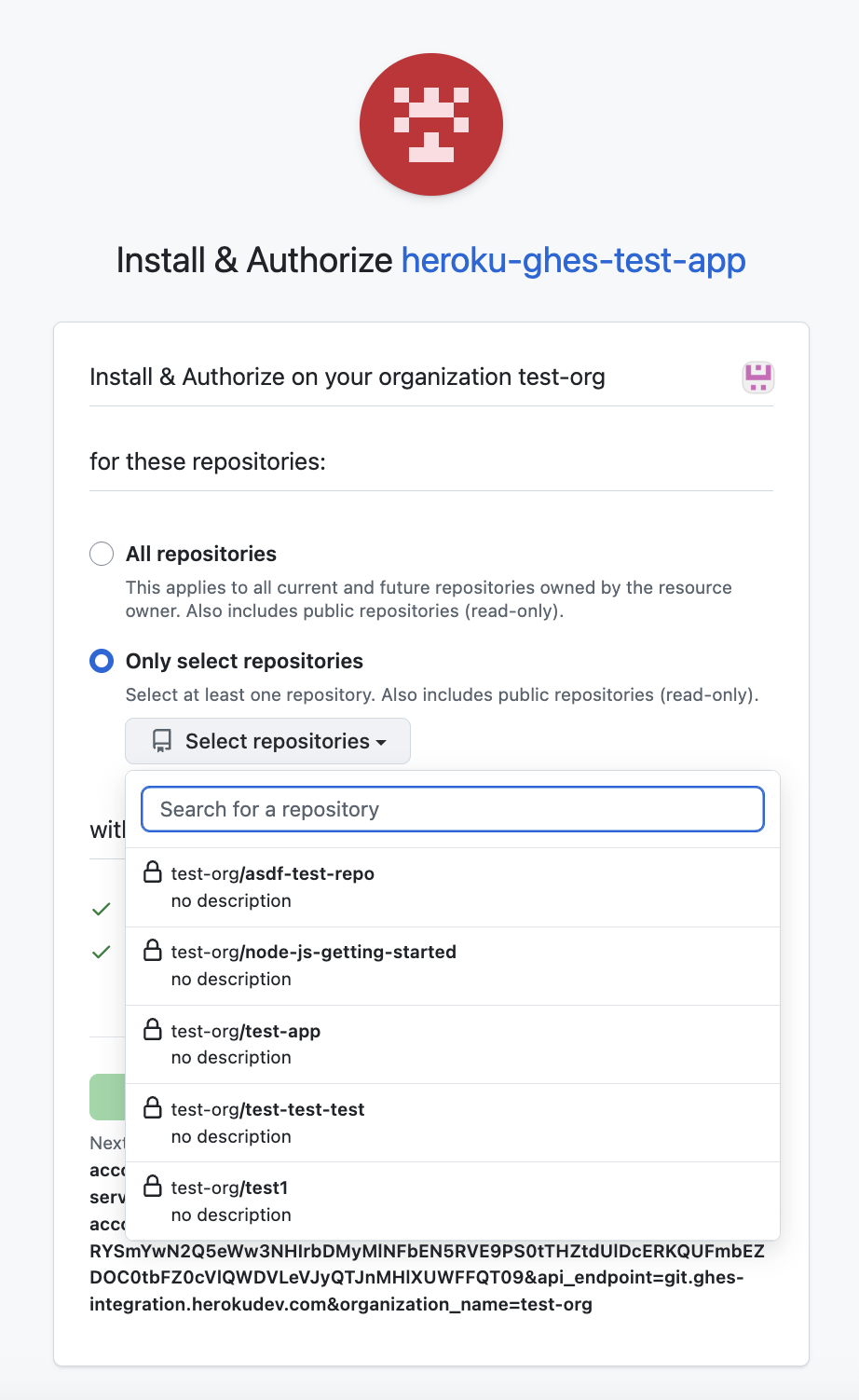
Select Install & Authorize to complete the installation process and return to dashboard.heroku.com.
After installing the integration on an Enterprise account, all Enterprise teams under that account must use this GitHub Enterprise Server integration for any new apps or pipelines.
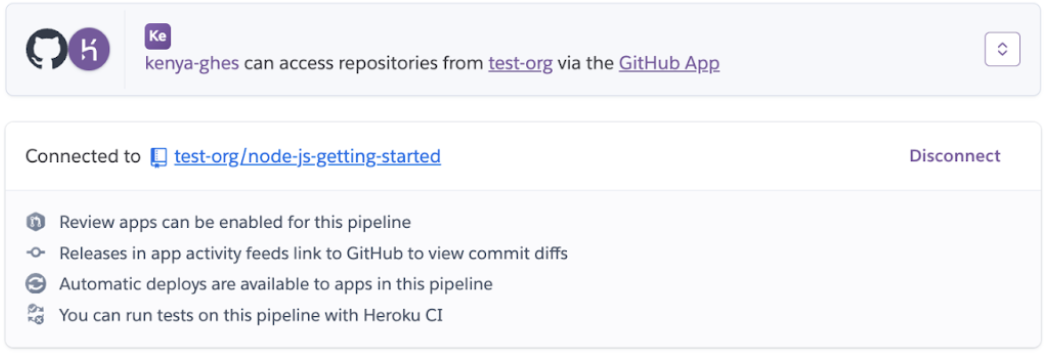
After installation is complete, the Settings tab updates to show the connected org:
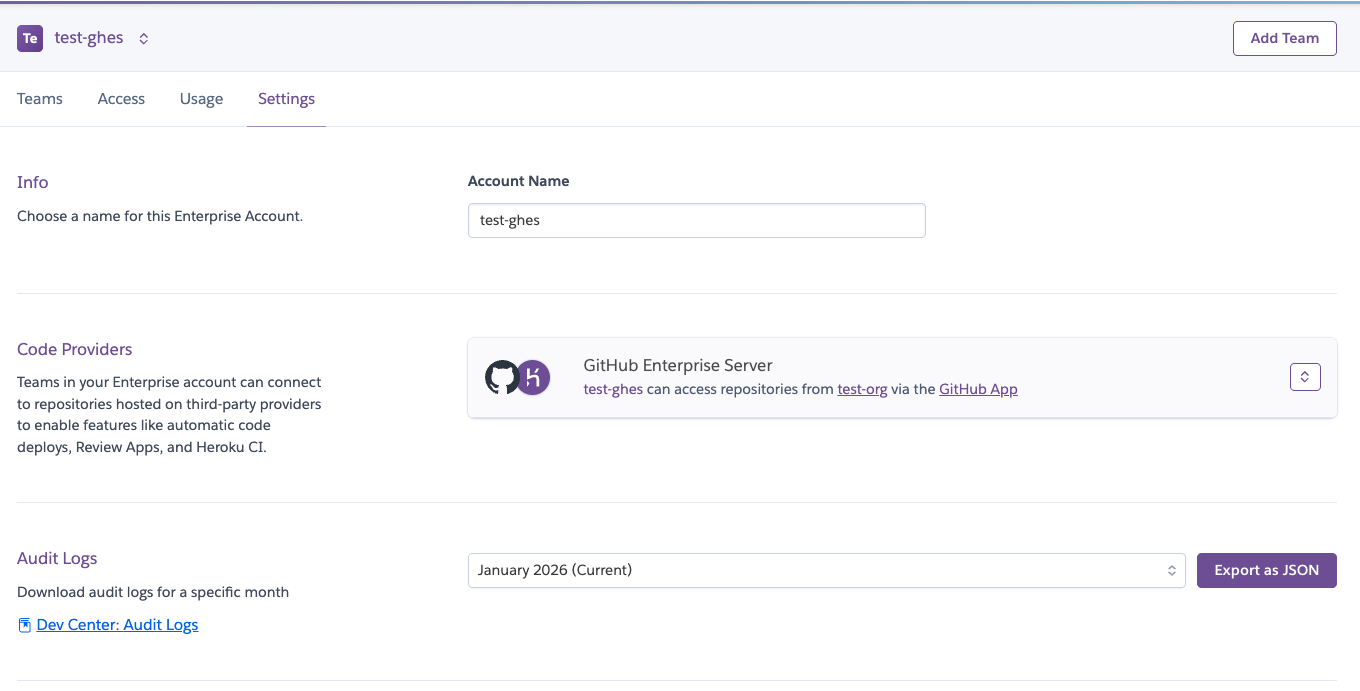
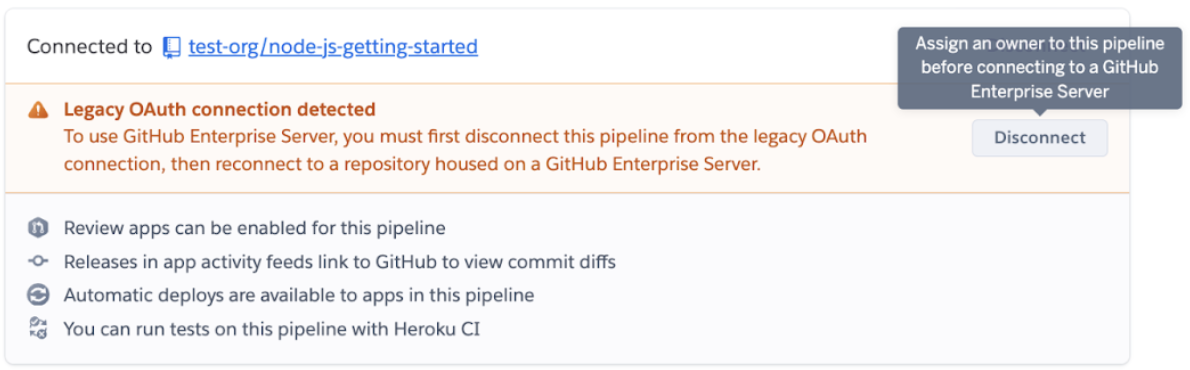
You can then reconfigure apps and pipelines to use the new GitHub app. Here’s an example of a pipeline’s Settings tab that uses the OAuth Heroku GitHub integration, with option to connect with the new integration instead:
Reconfigure Repo Access
To reconfigure an existing GitHub App installation for the Enterprise Server integration, go to the Settings tab of the Enterprise account.
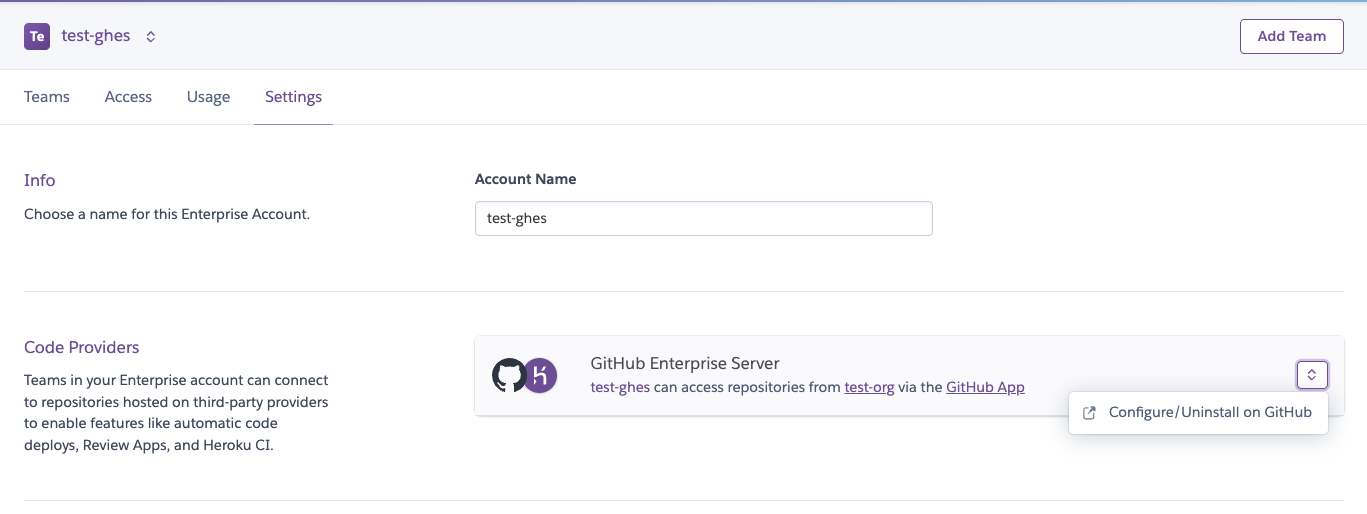
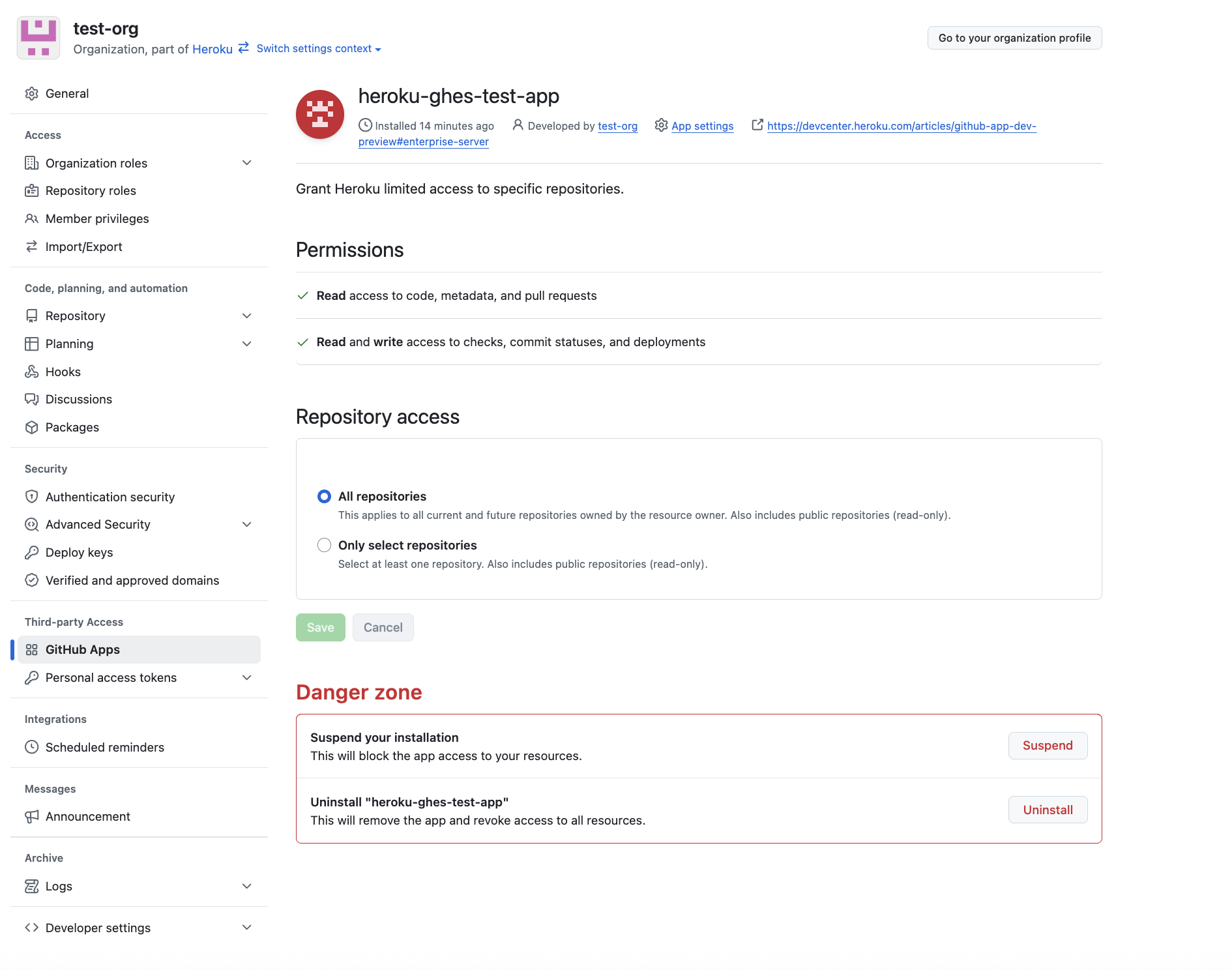
Select Configure/Uninstall on GitHub to get redirected to the GitHub App’s settings page where you can change the repository access or uninstall the GitHub App entirely:
View All Authorized Enterprise Server Orgs On Your Account
If you’re a member of more than one Enterprise Account using this new integration, you can see all the authorized GitHub apps in your account.
- Select
Account Settingsfrom under your profile - Select the
Applicationstab. - View the list of authorized GitHub apps and connected org in the
Third-Party Servicessection.
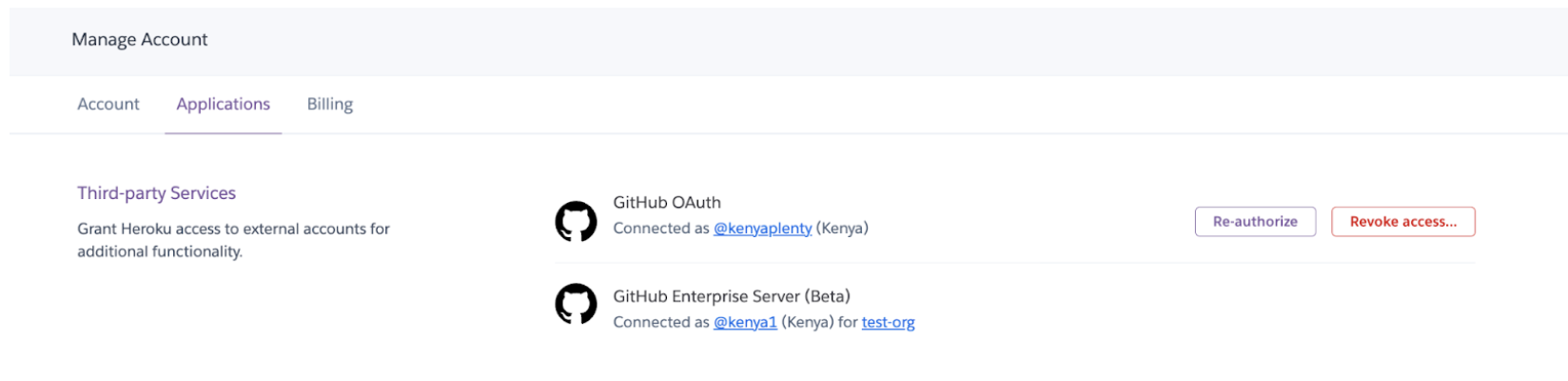
This example shows a user with the GitHub OAuth integration and the GitHub Enterprise Server integration. There’s no option to reauthorize or revoke access from GitHub Enterprise Server here because that integration is at the Enterprise account level, not your own account. To reauthorize, go the Enterprise account’s Settings tab. To revoke access, refer to Uninstalling the Integration.
Connect or Disconnect an App From a Repo
If your account is already connected to a GitHub Enterprise Server org, you can connect an individual app to a repo on it:
- Select the app from your dashboard.
- Go to the
Deploytab for the app. - Search for the repo to connect to.
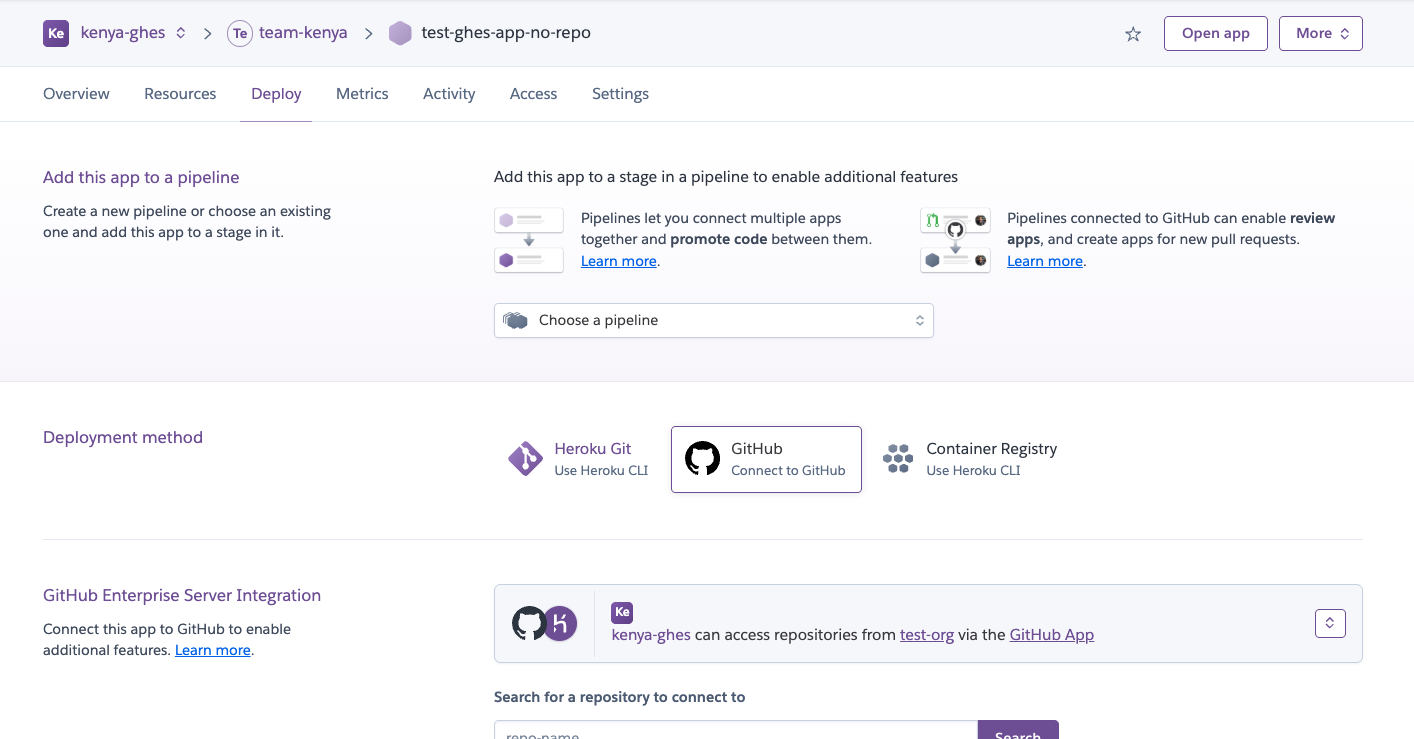
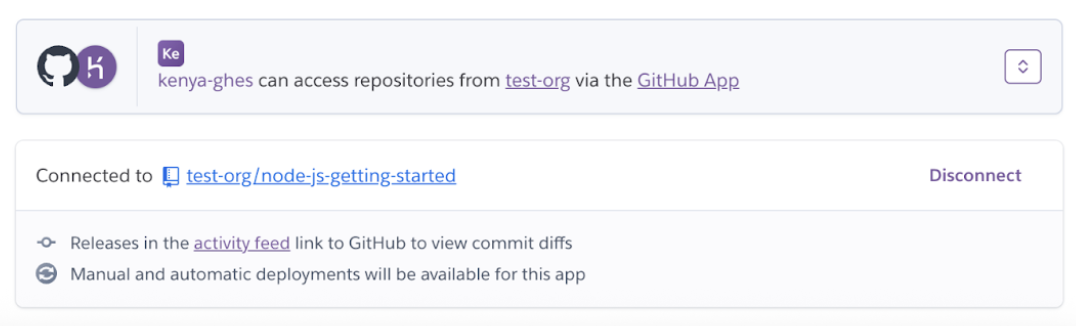
Select Disconnect to disconnect a repo from the app.
Connect or Disconnect a Pipeline From a Repo
If your account is already connected to a GitHub Enterprise Server org, you can connect a pipeline to a repo on it:
- Select the pipeline from your dashboard.
- Go to the
Settingstab for the pipeline. - Search for the repo to connect to.
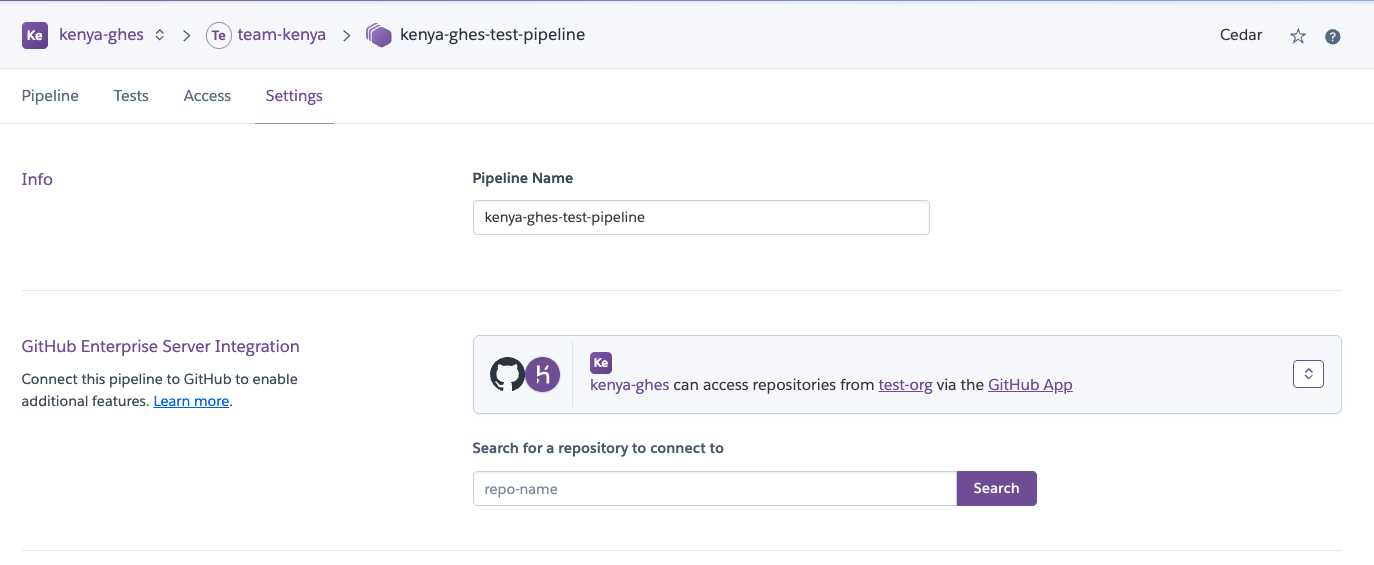
Select Disconnect to disconnect a repo from the pipeline.
Uninstall the Integration
Uninstalling disconnects all your pipelines and apps. You must manually connect apps and pipelines to the correct GitHub repo if you want to use personal OAuth tokens again.
To uninstall:
- Go to the
Settingstab of the Enterprise account - Select the dropdown in the GitHub Enterprise Server panel
- Select
Configure/Uninstall on GitHub

After redirecting to the GitHub App settings page, select Uninstall.
Limitations
You must disable the expiring user access tokens feature in GitHub Enterprise Server to allow for proper functioning of this integration. That feature forces users to log in every 8 hours to ensure that their credentials and access remain valid. Failure to do so results in 401 Unauthorized errors returned from the API when attempting to access information about the GitHub Enterprise Server and GitHub app. Currently, the Heroku dashboard doesn’t support handling these errors appropriately.
There’s a 1:1 relationship between your Enterprise account and GitHub org. If you have any pipelines using repositories outside the GitHub org, fork and move them to that main GitHub org before configuring the integration.
You can only link a GitHub org to one Enterprise account at a time. If you linked your GitHub org to an Enterprise Account, and want to link it to a different one, you have to uninstall the integration first.
This integration doesn’t work for GitHub orgs that restrict access by IPs.
Heroku Buttons won’t work with private repositories if the user trying to launch it doesn’t have access to the repos.